At What Age Do Kids Lose Their Baby Teeth: A Comprehensive Guide

As parents, we often wonder when our children will start losing their baby teeth. It’s a significant milestone in their development, and it’s essential to know when to expect it. Losing baby teeth is a natural process that happens to every child, but the timing can vary. This comprehensive guide will help parents understand when their children will start losing their baby teeth and what to expect during the process. The process of losing baby teeth is known as exfoliation. It starts around the age of six when the first set of permanent teeth begins to grow. The baby teeth act as placeholders for the permanent teeth and help guide them into their correct positions. As the permanent teeth grow, they dissolve the roots of the baby teeth, which eventually fall out. This process can take several years, and each child’s timeline is unique. Understanding when your child will start losing their baby teeth can help you prepare for the transition and ensure their dental health is on track.
Baby teeth, also known as primary teeth, are the first set of teeth that develop in a child’s mouth. These teeth typically begin to emerge between six and twelve months of age and continue to erupt until the child is about three years old. There are twenty primary teeth in total, ten on the top and ten on the bottom. These teeth are important for a child’s development as they help with speech, chewing, and maintaining proper spacing for adult teeth. As children grow, their baby teeth will begin to loosen and fall out, making way for permanent teeth to come in. This process typically begins around the age of six and continues until the child is around twelve years old. While the loss of baby teeth is a normal part of growing up, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene habits to ensure the health of both primary and permanent teeth.
Understanding when kids lose their baby teeth is crucial for parents and caregivers as it helps them prepare for the developmental changes of their child. The shedding of baby teeth is a natural and exciting milestone in a child’s life, but it can also be a stressful time for both the child and their caretakers. Knowing when to expect the first tooth to fall out and when all of them should be replaced by adult teeth can help parents anticipate any potential dental issues and seek professional advice if necessary. Additionally, it can be an opportunity to celebrate the growth and development of the child and help them feel confident and proud of their changing appearance.
The Basics of Baby Teeth
Baby teeth, also known as primary teeth, are the first set of teeth that emerge in a child’s mouth. They typically begin to appear between 6-12 months of age and continue to erupt until around age three. Baby teeth play a crucial role in a child’s overall dental development, as they help with speech development, chewing, and also aid in the alignment and spacing of permanent teeth. In total, children will have 20 primary teeth, ten on the top and ten on the bottom. It’s important to take good care of baby teeth, as they are susceptible to decay and other dental issues. Parents should begin brushing their child’s teeth as soon as they appear, using a soft-bristled brush and a small amount of fluoride toothpaste. Children should also visit the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. As baby teeth begin to fall out and permanent teeth come in, it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene habits to ensure a healthy smile for years to come.
Baby teeth, also known as primary teeth, are the first set of teeth that develop in children. These teeth typically start to emerge between the ages of six months to one year and are usually fully developed by the age of three years. Baby teeth are important for many reasons, including allowing children to chew food properly, aiding in speech development, and maintaining the proper spacing for permanent teeth. Children will typically have 20 baby teeth, 10 on top and 10 on bottom, which will eventually fall out to make way for their adult teeth. It is important for parents to take good care of their child’s baby teeth by encouraging regular brushing and dental checkups, as healthy baby teeth are crucial for the proper development of their permanent teeth.
Children typically have 20 baby teeth, also known as primary teeth. These teeth start to emerge through the gums around six months of age, and they typically fall out between the ages of six and 12. Baby teeth are important for a child’s development, as they help them chew their food and speak clearly. Once a child’s permanent teeth start to come in, they begin to push out the baby teeth. This process can take several years to complete, and it’s important to monitor a child’s dental health during this time to ensure that their permanent teeth come in correctly.
Baby teeth, also known as primary teeth, usually start to appear in infants between the ages of six and twelve months. However, some children may start teething earlier or later than this age range. The two front teeth on the bottom are usually the first to come in, followed by the four upper front teeth. By age three, most children have a full set of 20 baby teeth. It’s important to take care of baby teeth, as they are essential for chewing, speaking and holding space for adult teeth.
When Do Kids Start Losing Their Baby Teeth?
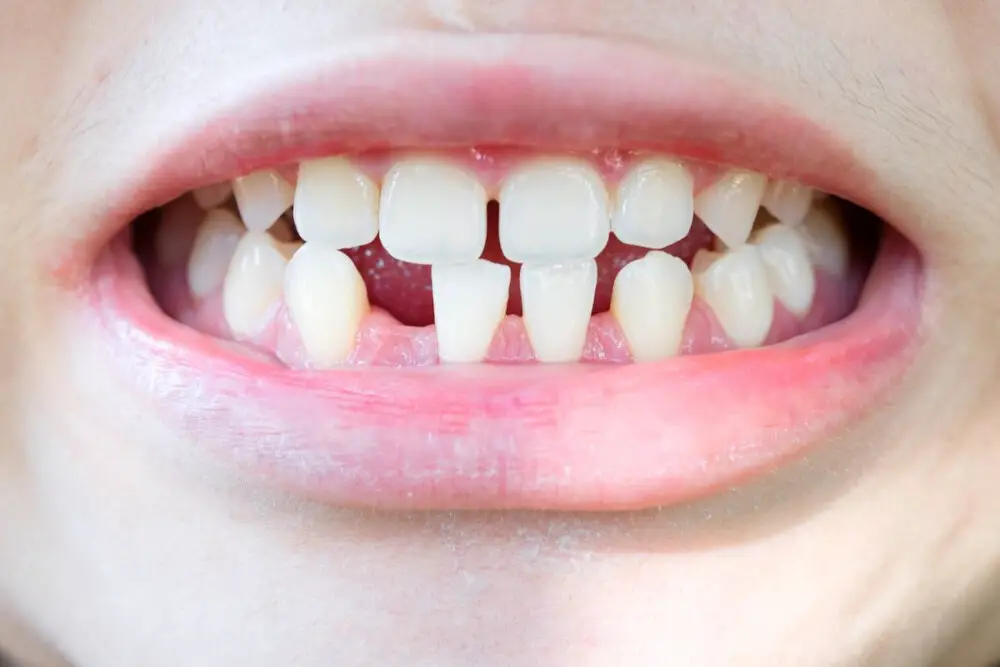
Losing baby teeth is a natural part of a child’s development, and it usually begins around the age of six or seven years old. However, some children may start losing their baby teeth as early as four years old or as late as eight years old. The process of losing baby teeth typically continues until the age of 12 or 13 when all of the permanent teeth have grown in. Generally, the lower teeth tend to fall out before the upper teeth, and the front teeth tend to fall out before the back teeth. The process of losing baby teeth can be an exciting time for children, but it can also be a bit scary or uncomfortable. Children may experience some discomfort or pain as their baby teeth begin to loosen and fall out. Parents can help their children by encouraging them to wiggle their loose teeth gently and by providing them with soft foods to eat during this time. It is also important to remind children about the importance of good oral hygiene, especially as they begin to grow their permanent teeth. By following a healthy dental routine, children can ensure that their permanent teeth come in strong and healthy, setting them up for a lifetime of good oral health.
The average age range for losing baby teeth is between 6 to 12 years old. This process is known as exfoliation, where the roots of the baby teeth start to dissolve, making the teeth loose and eventually fall out. The timeline for exfoliation varies for each child, but it generally starts with the lower front teeth, followed by the upper front teeth, and then the molars. The process can be accompanied by mild pain and discomfort, but it is a natural part of the child’s development and a sign that their permanent teeth are growing in. Parents can help ease the discomfort by encouraging their child to eat soft foods and using over-the-counter pain relievers if necessary.
The timeline for children losing their baby teeth can vary, but there are several factors that can influence when this process begins and ends. Genetics play a crucial role, as children tend to follow the same pattern as their parents did when they lost their teeth. Nutrition is also a significant factor, as children who consume a diet high in sugar and carbohydrates may experience tooth decay, which can lead to premature tooth loss. Additionally, certain medical conditions such as hypothyroidism and celiac disease can affect the timing of tooth loss. Finally, early loss of primary teeth due to injury or decay may result in delayed eruption of permanent teeth. Parents can help ensure their child’s teeth remain healthy and develop normally by encouraging a balanced diet, regular dental checkups, and good oral hygiene habits.
When it comes to the timing of losing baby teeth, there may be some differences between girls and boys. Generally, girls tend to lose their baby teeth earlier than boys. This may be due to several factors, including hormonal differences, genetic makeup, and dietary habits. For example, studies have shown that girls tend to develop faster than boys in terms of physical and cognitive development, which may contribute to earlier tooth loss. Additionally, girls may have better oral hygiene habits or consume less sugary foods, which can promote healthy teeth and gums. However, it’s important to note that every child is different, and there may be significant variations in the timing of tooth loss regardless of gender.
What Order Do Baby Teeth Fall Out In?
Losing baby teeth is an essential part of a child’s development, and it typically occurs between the ages of six and twelve years old. The sequence in which a child’s baby teeth fall out is relatively consistent, although there may be slight variations. Generally, the first baby teeth to fall out are the lower front teeth, followed by the upper front teeth. These are often referred to as the central incisors. Next, the lateral incisors, which are located next to the central incisors, will fall out. The first molars will then follow, and finally the canines and second molars. The process of losing baby teeth usually takes a few years, and every child’s experience will be unique. It’s important to note that the order in which baby teeth fall out can vary slightly from child to child. However, if your child’s baby teeth aren’t falling out in the expected order, it’s essential to consult with a dentist. Additionally, it’s crucial to ensure that your child is brushing and flossing their teeth regularly and maintaining good oral hygiene practices. This will help to ensure that their adult teeth grow in healthy and strong and that they have a bright and healthy smile for years to come.
The chart of the typical order of tooth loss provides an essential guide for parents and caregivers to help them understand the natural process of their child’s dental development. The chart outlines the sequence of tooth loss, starting from the lower central incisors to the second molars, and then the upper teeth follow the same pattern. The first baby teeth usually fall out around the age of six and continue until the child is twelve or thirteen years old. Although the timing of tooth loss may vary from child to child, having a general understanding of the sequence can help parents anticipate when their child may need dental care or orthodontic treatment. It is essential to keep track of the baby teeth’s loss to ensure that permanent teeth come in correctly and avoid any dental problems in the future.
While the standard order of losing baby teeth is generally predictable, there are some exceptions to the norm. Children with certain medical conditions such as Down syndrome or cleft palate may experience delayed tooth eruption or have additional teeth that need to be removed. Additionally, trauma to the mouth or injury to the teeth can cause them to fall out prematurely. In some cases, genetics can also play a role in the timing of tooth loss. It’s important for parents to monitor their child’s dental development and consult with a dentist if they have any concerns or notice any abnormalities.
What Happens After Baby Teeth Fall Out?
After a child loses their baby teeth, the body begins a natural process of replacing them with permanent teeth. This process typically begins around the age of six or seven and continues through adolescence. During this time, the permanent teeth grow in and replace the baby teeth that have fallen out. The first molars are usually the first permanent teeth to appear, followed by the front teeth and then the second molars. As the permanent teeth grow in, it’s important to maintain good dental hygiene habits to ensure their health and longevity. Brushing and flossing regularly, as well as visiting the dentist for checkups and cleanings, are essential steps in maintaining healthy teeth and gums. Additionally, it’s important to avoid habits that can damage the teeth, such as chewing on hard objects or using the teeth to open packaging. With proper care and attention, the new permanent teeth can last a lifetime.
Permanent teeth, also known as adult teeth, replace the baby teeth that fall out. These teeth start to appear around the age of six and continue to develop until the age of 21. There are a total of 32 permanent teeth which include 16 on the top and 16 on the bottom, and they are larger and stronger than baby teeth. The permanent teeth are made up of four different types of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. Each tooth has a specific function, from biting and tearing to grinding and chewing food. It is important to take care of these teeth through proper dental hygiene as they will last a lifetime.
Caring for permanent teeth is crucial to maintain good oral health and prevent dental problems in the long run. It is essential to brush teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles that can cause decay. Eating a balanced diet and avoiding sugary and acidic foods and drinks can also help prevent tooth decay. Regular visits to the dentist for check-ups and cleanings are recommended to identify and treat any dental issues early on. Protecting teeth during sports or other activities with a mouthguard can also prevent damage or loss of permanent teeth. By following these simple steps, you can keep your permanent teeth healthy and strong for a lifetime.
Losing baby teeth is a natural and exciting part of a child’s development. Children typically begin losing their baby teeth around the age of 6, with the process continuing until around the age of 12. The first teeth to go are usually the lower front teeth, followed by the upper front teeth. The timing of tooth loss can vary from child to child, but it is important to ensure that proper dental care is being provided to promote healthy oral hygiene habits. Parents can support their children during this time by making sure they have a balanced diet, encouraging regular brushing and flossing, and scheduling regular dental check-ups. With proper care, children can enjoy a healthy and happy smile as they grow and develop.
Regular dental checkups for kids are crucial to ensure their oral health and hygiene. It is recommended that children have their first dental visit by age one or as soon as their first tooth appears. These checkups allow the dentist to monitor the development of their teeth, identify any potential issues early on, and provide preventive care such as dental cleanings and fluoride treatments. Additionally, regular dental checkups help children establish good oral hygiene habits and reduce the risk of developing cavities and other oral health problems. By making dental checkups a regular part of your child’s healthcare routine, you can help them maintain a healthy and happy smile for years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, losing baby teeth is a natural and exciting milestone in a child’s development. Although the timing can vary from child to child, the average age for losing baby teeth is between 5 and 7 years old. It’s important for parents and caregivers to be aware of the signs of tooth loss and to encourage good dental hygiene habits from a young age. By providing proper dental care and support, children can maintain healthy teeth and gums throughout their lives. As children grow and transition to permanent teeth, it’s important to continue to monitor their dental health and address any concerns with a dental professional. Losing baby teeth is just one step in a child’s journey towards a healthy and happy future.