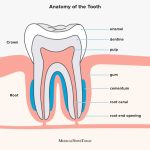
At What Age Do You Start Losing Teeth? Understanding the Natural Process of Tooth Shedding
As we grow up, our bodies go through a lot of changes, and one of the most significant changes is the loss of baby teeth. Tooth shedding is a natural process that occurs as our permanent teeth begin to emerge. It is a gradual and continuous process that usually begins in early childhood and can last until the late teenage years. Understanding the process of tooth shedding is essential for parents and caregivers to ensure proper dental care for their children. The process of tooth shedding is a fascinating one that involves several stages. The first stage is when the baby teeth gradually become loose, and the roots start to dissolve. This process is triggered by the growth and development of the permanent teeth that are pushing against the roots of the baby teeth. As the roots dissolve, the baby teeth become even looser, and eventually, they fall out. In some cases, the baby teeth may need to be removed by a dentist if they do not fall out naturally.
Understanding the natural process of tooth shedding is crucial for both parents and children. Tooth shedding is a natural process that begins around the age of six and can continue until the age of 12 or 13. It is important to understand that this process is normal and not a cause for concern. It is also important to understand that the way in which teeth are lost can affect the development of adult teeth. Parents should be aware of the timing of tooth loss so that they can help their children take care of their teeth and be prepared for when adult teeth begin to emerge. Additionally, understanding the tooth shedding process can help parents detect any issues with their child’s dental health, such as overcrowding or impacted teeth, and seek treatment if necessary. Overall, understanding the natural process of tooth shedding is essential for maintaining good dental health and ensuring proper development of adult teeth.
Tooth shedding, also known as exfoliation, is a natural process where primary teeth or baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth. This process usually begins around the age of six and continues until the early teenage years. As the permanent teeth grow, the roots of the primary teeth dissolve, causing them to become loose and eventually fall out. The permanent teeth then move into place and take over the function of the baby teeth. Tooth shedding is an important part of dental development and ensures that the mouth has enough space for the permanent teeth to grow in properly. While it can be a bit uncomfortable for children, it is a completely normal and necessary process that leads to a healthy, functional adult smile.
Primary Teeth

Primary teeth, also known as baby teeth or milk teeth, are the first set of teeth that develop in humans, typically appearing between 6 to 10 months of age. These teeth serve as placeholders for the permanent teeth that will eventually replace them. Primary teeth are essential for a child’s proper speech development, chewing and biting, and maintaining the space necessary for the permanent teeth to grow. On average, children have 20 primary teeth, consisting of four incisors, two canines, and four molars on both the upper and lower jaw. Primary teeth begin to shed naturally around the age of 6, and the process can continue until the age of 12 or 13. The shedding process is a natural part of dental development and is necessary for the permanent teeth to grow correctly. The roots of the primary teeth dissolve, and the teeth become loose, eventually falling out to make room for the permanent teeth to emerge. The order in which primary teeth shed varies, but typically the first teeth to be lost are the lower central incisors, followed by the upper central incisors, and then the lateral incisors, canines, and molars. It is essential to encourage good oral hygiene habits during this time to prevent any complications that may arise during the transition from primary to permanent teeth.
Primary teeth, also known as baby teeth, are the first set of teeth that develop in a child’s mouth. These teeth typically start to emerge around the age of six months and are usually fully developed by the age of three. The primary teeth serve several important purposes, including helping children learn to chew their food, aiding in proper speech development, and maintaining the space needed for permanent teeth to grow in properly. Additionally, primary teeth play a critical role in the development of a child’s jaw and facial structure, providing a foundation for the adult teeth that will eventually replace them. While primary teeth are eventually shed and replaced by permanent teeth, they are still an essential part of a child’s oral health and development.
The average age range for primary teeth to begin shedding is between 6 and 7 years old. This process, also known as exfoliation, is a natural occurrence that happens as the permanent teeth begin to grow and develop. While the exact timing can vary from child to child, the process typically begins with the lower front teeth and progresses to the upper front teeth. As the permanent teeth push up from beneath the gums, they eventually dissolve the roots of the primary teeth, causing them to become loose and fall out. It is important for parents to monitor their child’s teeth during this time and ensure that they are properly caring for their new permanent teeth as they emerge.
Primary teeth, also known as baby teeth or milk teeth, are gradually replaced by permanent teeth through a natural process called tooth shedding. This process usually begins around the age of 6 and continues until the late teen years. As the permanent teeth develop, they start to push against the roots of the primary teeth, causing them to become loose and eventually fall out. The roots of the primary teeth then dissolve, making way for the permanent teeth to emerge. The order in which the permanent teeth come in varies from person to person, but the process generally follows a predictable pattern. While tooth shedding can be a bit uncomfortable, it is a completely normal and necessary part of dental development.
Permanent Teeth
Permanent teeth are the set of teeth that replace the primary teeth. They are the final set of teeth that an individual will have for their lifetime. These teeth are larger and stronger than the baby teeth and are designed to last for decades. The permanent teeth generally emerge between the ages of 6 and 13 years, with the exception of wisdom teeth, which may emerge later. A total of 32 permanent teeth, including four wisdom teeth, will emerge in adulthood. The permanent teeth are comprised of four types of teeth, including incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. Incisors are the eight teeth located in the front of the mouth and are used for biting into food. Canines are the four pointed teeth located next to the incisors and are used for tearing food. Premolars are the eight teeth located next to the canines and are used for chewing and grinding food. Finally, molars are the twelve teeth located in the back of the mouth and are also used for chewing and grinding food. It is essential to take good care of permanent teeth as they are the only set that an individual will have for their lifetime.
Permanent teeth are the set of teeth that replace the primary teeth and are meant to last a lifetime. They typically start to emerge between the ages of six and twelve, and there are a total of 32 permanent teeth in the adult mouth. These teeth are made up of four different types: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. Each type of tooth has a specific purpose in the mouth, from cutting and tearing food with the sharp incisors and canines, to grinding and crushing with the flat molars. The permanent teeth are essential for maintaining oral health, as they not only help with eating and speaking, but also support the structure of the face and jaw. Proper dental care, including regular brushing and flossing, is necessary to ensure the longevity and health of these important teeth.
The process of tooth shedding is a natural and essential phenomenon that occurs in everyone’s life. The average age range for permanent teeth to begin shedding is between 17 and 25 years old, which is the time when the wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, usually start to emerge. Wisdom teeth are located at the back of the mouth and can cause discomfort and pain if they don’t have enough space to grow or if they grow in an improper direction. In some cases, they may need to be extracted by a dentist to prevent further complications. It’s important to understand that the timing and process of tooth shedding can vary from person to person and that regular dental check-ups can help detect any potential issues early on.
While most people lose their wisdom teeth between the ages of 17 and 25, some individuals may not experience this natural process. This is because the size and shape of the jawbone can vary from person to person, leading to differences in the amount of space available for teeth. In some cases, the jaw may be large enough to accommodate wisdom teeth without causing crowding or discomfort, while in others, there may simply not be enough room for them to erupt. Additionally, genetics can play a role in whether or not a person loses their wisdom teeth, as some people may inherit traits that make it less likely for these teeth to develop or emerge. Ultimately, the decision to remove wisdom teeth should be based on individual factors such as oral health and personal preference, rather than a predetermined timeline.
Factors Affecting Tooth Shedding
Tooth shedding, also known as exfoliation, is a natural process that occurs in humans throughout their lifetime. It involves the gradual loss of primary teeth and their replacement with permanent teeth. The timing of tooth shedding varies from person to person, but it generally starts around the age of 6 and continues until the early teenage years. There are several factors that can affect tooth shedding, including genetics, nutrition, oral hygiene, and dental injuries. Genetics play a significant role in tooth shedding. The timing of tooth eruption and shedding is largely influenced by genetic factors. If a child’s parents experienced early or delayed tooth shedding, it’s likely that their child will experience the same. Nutrition is also an essential factor in tooth shedding. A diet lacking in essential vitamins and minerals, particularly calcium and vitamin D, can delay the eruption and shedding of teeth. Poor oral hygiene can lead to tooth decay and gum disease, which can cause premature tooth loss. Additionally, dental injuries, such as blunt force trauma or a sports injury, can cause teeth to loosen or fall out prematurely. It’s important to maintain good oral health and seek prompt treatment for any dental injuries to ensure proper tooth shedding.
Genetics and family history play a significant role in the natural process of tooth shedding. The timing and sequence of primary tooth loss can be influenced by a child’s genetic makeup, as well as the dental history of their parents. Studies have shown that children whose parents experienced early tooth loss tend to lose their teeth earlier than those whose parents had a later tooth loss. Additionally, genetic factors can also affect the development and eruption of permanent teeth, which can impact the timing and sequence of their shedding. Understanding the role of genetics and family history in tooth shedding can help parents and dentists better anticipate and manage this natural process.
Nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining overall health, including oral health. A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, such as calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus, can help strengthen teeth and bones. Consuming sugary or acidic foods and drinks can increase the risk of tooth decay and erosion, leading to tooth loss. Additionally, poor nutrition can weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections, including those that affect the gums and teeth. Therefore, it is essential to maintain a balanced and nutritious diet to ensure healthy teeth and gums, as well as overall well-being.
Maintaining dental hygiene habits is crucial for preventing tooth loss and maintaining good oral health. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily can help remove plaque and food particles that can lead to tooth decay and gum disease. It is also important to visit a dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups to detect any potential issues early on. Additionally, a healthy diet that is low in sugar and high in calcium and vitamin D can help keep teeth strong and healthy. By practicing good dental hygiene habits from a young age, you can help ensure that you keep your natural teeth for as long as possible.
Trauma or injury to the mouth can be a painful and unsettling experience. It can occur due to a fall, accident, or sports-related activity. The impact can result in broken, chipped, or knocked-out teeth, as well as damage to the gums and jaw. Such injuries can be particularly distressing for children who are in the process of losing their baby teeth. Trauma to the mouth can affect the natural process of tooth shedding, leading to delays or complications. It is important to seek immediate medical attention in case of any mouth injury to minimize the risk of long-term damage and ensure proper healing.
Dental Care During Tooth Shedding

During the process of tooth shedding, proper dental care is crucial to prevent any potential complications. It is recommended to start brushing your child’s teeth as soon as the first tooth appears, and to continue twice a day until all the baby teeth have fallen out. During this time, it is important to use a soft-bristled toothbrush and a fluoride toothpaste to prevent tooth decay and gum disease. As the baby teeth loosen and fall out, it is also important to encourage your child to brush gently around the area to avoid any discomfort or bleeding. In addition to brushing, regular dental check-ups are essential during tooth shedding. These appointments can help detect any potential issues and ensure that the permanent teeth are growing in properly. Dentists can also offer advice on how to care for your child’s teeth during this time, such as recommending a mouthguard for sports activities or suggesting orthodontic treatment if necessary. By taking proper care of your child’s teeth during tooth shedding, you can help ensure a healthy smile for years to come.
Regular dental checkups during tooth shedding are crucial to ensure that children’s teeth grow correctly and remain healthy throughout their lives. The shedding process can be a vulnerable time for teeth, as they are more susceptible to decay and infection. Regular checkups allow dental professionals to monitor the progress of tooth development and identify any potential issues early on. This enables them to provide the necessary treatment, such as cleaning or filling cavities, before they develop into more severe problems. Additionally, regular checkups provide an opportunity for parents to discuss their child’s dental health, including brushing and flossing habits, with their dentist, ensuring that they are taking the necessary steps to maintain their child’s oral hygiene. Ultimately, investing in regular dental checkups during tooth shedding can help ensure that children have a healthy and beautiful smile for years to come.
Maintaining good dental hygiene during tooth shedding is crucial to avoid dental problems in the future. Parents should teach their children the importance of brushing their teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing regularly, and rinsing with mouthwash. They should also encourage their children to eat a balanced diet, limit sugary snacks and drinks, and avoid using their teeth as tools. It is essential to continue regular dental checkups during tooth shedding to ensure that the new teeth are growing correctly and to identify any potential problems early. Additionally, parents should teach their children to be gentle with their gums during tooth shedding and avoid picking or pulling on loose teeth to avoid irritation and infection. By following these tips, parents can help their children maintain good dental health during the natural process of tooth shedding.
Tooth shedding is a natural process that occurs in children as they make way for their permanent teeth. However, if tooth shedding is not monitored properly, it can lead to potential complications. One common issue is overcrowding, where the permanent teeth do not have enough space to grow, causing misalignment and crooked teeth. This can also lead to bite problems, difficulty chewing, and speech problems. Additionally, if baby teeth are not shed properly, they may not fall out at all, causing the permanent teeth to come in crooked or even not at all. It is essential to monitor tooth shedding to ensure that the permanent teeth come in correctly and prevent future dental complications.
\Tooth shedding is a natural process that occurs in all humans, and it starts at the age of 6 or 7. The first teeth to fall out are usually the lower front teeth, followed by the upper front teeth. The process continues until all 20 baby teeth have been replaced by permanent teeth. The shedding of baby teeth is a gradual process that lasts until the age of 12 or 13. However, some people may experience delayed shedding or premature tooth loss due to various reasons such as genetics, trauma, or certain medical conditions. It’s important to maintain good oral hygiene and seek dental care regularly to ensure healthy teeth and gums throughout life.\
Understanding the tooth shedding process is crucial for maintaining overall dental health. The natural process of tooth shedding is a vital part of tooth development and growth. The shedding of baby teeth is a natural and necessary process that makes way for the permanent teeth to grow in. It is important to understand the timing of this process and be able to identify any abnormalities or issues that may arise. Any disruption in the tooth shedding process can lead to dental complications, including overcrowding, misalignment, and decay. Therefore, it is important to monitor the shedding process and seek professional dental care if necessary to ensure optimal dental health.
Maintaining good dental hygiene habits is essential for healthy teeth and gums. One of the best ways to ensure that your teeth remain in good condition is by scheduling regular dental checkups. These checkups can help identify any potential problems and prevent them from becoming serious issues. Brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing regularly, and avoiding sugary foods and drinks can also help keep your teeth healthy. Remember, taking care of your teeth is an investment in your overall health and well-being. So, make sure to prioritize your dental hygiene and schedule those regular checkups to keep your smile shining bright for years to come.
Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding the natural process of tooth shedding is essential for maintaining good oral health. Children typically start losing their baby teeth around the age of six, and this process continues until the age of 12 or 13. The permanent teeth that replace the baby teeth are important for chewing and speaking, and it is crucial to take care of them by practicing good oral hygiene habits such as brushing and flossing regularly. While losing teeth can be a bit scary for children, it is a natural part of growing up and should be celebrated as a milestone in their development. By taking care of their teeth, children can enjoy a healthy and beautiful smile for years to come.