Understanding Tooth Development: When Do Kids Start Losing Teeth?
Tooth development in children is a fascinating process that marks an important milestone in their growth and development. While most parents eagerly await the arrival of their child’s first tooth, they are often left wondering when their little one will start losing them. Understanding the timeline of tooth development and eruption can help parents prepare for the changes that lie ahead and ensure their child’s dental health is properly cared for. The process of tooth development begins before a child is even born. The buds for all 20 primary teeth are formed in the gums during the first trimester of pregnancy. These teeth typically begin to emerge between 6 and 12 months of age, with the lower front teeth usually appearing first. As children grow and develop, their jaws and facial structures change, making room for the larger permanent teeth to replace the smaller primary teeth. This process, known as exfoliation, typically begins around age 6 and continues into the teenage years. Understanding when primary teeth are lost and replaced by permanent teeth can help parents ensure their child’s dental health is properly maintained during this transitional period.
Understanding tooth development is crucial for parents, dentists, and anyone involved in the care of children’s oral health. The process of tooth development is complex and involves numerous stages, beginning in the womb and continuing through childhood and adolescence. By understanding tooth development, parents can help their children maintain healthy teeth and gums and identify any issues early on. Dentists can use their knowledge of tooth development to provide appropriate treatments and interventions to prevent and address dental problems. Overall, a comprehensive understanding of tooth development is essential for promoting good oral health and ensuring that children maintain healthy and beautiful smiles throughout their lives.
Primary teeth, also known as baby teeth, are a set of 20 teeth that begin to develop in the womb and usually erupt between the ages of 6 months to 3 years. These teeth play a crucial role in a child’s ability to chew, speak, and maintain proper facial structure. On the other hand, permanent teeth, also known as adult teeth, begin to develop beneath the gums around the age of 6 and continue to erupt until the late teenage years. Unlike primary teeth, permanent teeth are meant to last a lifetime and there are 32 in total. They are larger and stronger than primary teeth and serve a more significant role in the digestion process. Understanding the differences between primary and permanent teeth is essential for parents to ensure proper oral care and development for their children.
The Process of Tooth Development

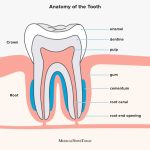
Tooth development is a complex biological process that starts during fetal development and continues until the age of 25-30 years. The process involves the formation of hard tissues such as enamel, dentin, and cementum, which comprise the different parts of a tooth. The process is regulated by a variety of genetic and environmental factors, and any disruption in this process can lead to various dental abnormalities such as tooth decay, malocclusion, and tooth loss. Tooth development starts with the formation of tooth buds, which are clusters of mesenchymal and epithelial cells that give rise to the different structures of a tooth. As the tooth buds grow, they form a cap-like structure that encloses the dental papilla, which is the precursor to the dentin and pulp. The enamel organ, which is the precursor to the enamel, is formed on the surface of the dental papilla, and the cementum-forming cells are derived from the dental follicles. The different stages of tooth development are characterized by the proliferation, differentiation, and mineralization of these different dental tissues, and the process is tightly regulated by signaling molecules such as BMPs, Wnts, and FGFs. Understanding the process of tooth development is important for the diagnosis and treatment of various dental conditions, and it can help to improve oral health outcomes in children and adults alike.
Tooth development begins early in fetal life with the formation of tooth buds. These buds are groups of cells that arise from the dental lamina, a band of epithelial tissue in the developing jaw. As the buds grow and divide, they begin to differentiate into the various types of teeth, such as incisors, canines, and molars, each with its unique shape and function. This process is tightly regulated by signaling molecules and genetic factors, which guide the cells along their developmental pathways. By the time a child is born, all of their primary teeth are present as tooth buds, ready to erupt and begin the process of chewing and speech development.
The eruption of primary teeth, also known as baby teeth, is an essential aspect of a child’s dental development. This process typically begins around six months of age and continues until the child is around three years old, resulting in a total of 20 primary teeth. As the teeth emerge from the gums, the child may experience discomfort or pain, which can be relieved by gentle massaging or a cold teething ring. It’s crucial to take care of primary teeth, as they play a crucial role in the child’s ability to speak, eat, and maintain proper oral hygiene. Furthermore, primary teeth act as placeholders for permanent teeth, helping to guide them into their proper positions as they grow.
The formation and eruption of permanent teeth is a complex process that involves multiple stages. It all starts with the development of tooth buds, which form in the gums during early childhood. These buds eventually grow into fully-formed teeth, which begin to push their way through the gums and into the mouth. As the teeth continue to grow, they become anchored into the jawbone, allowing them to withstand the forces of biting and chewing. Over time, the roots of the teeth continue to grow and strengthen, eventually becoming fully mature. Finally, as children reach their teenage years, their permanent molars begin to emerge, completing their set of adult teeth. While this process may seem simple on the surface, it is actually quite complex, involving a wide range of biological processes and intricate interactions between various cells and tissues in the body.
When Do Kids Start Losing Teeth?
The process of losing teeth is an essential and exciting developmental milestone for children. Generally, children start losing their baby teeth between the ages of 5 and 7 years old. The first teeth to fall out are usually the front lower teeth, followed by the front upper teeth. By the time a child reaches the age of 13, they will most likely have lost all their baby teeth, and their permanent teeth will have grown in their place. However, the timing of losing teeth varies from child to child, and some children may lose their baby teeth earlier or later than others. The process of losing baby teeth is a natural part of tooth development, and it occurs because the permanent teeth underneath the baby teeth are ready to grow in their place. The roots of the baby teeth dissolve, allowing them to fall out and make room for the permanent teeth. This process can be exciting for children, as it is a sign that they are growing up and becoming more independent. Parents and caregivers can help make this transition smoother for children by providing them with adequate dental care and reassuring them that losing their baby teeth is a normal part of their development.
The process of losing primary teeth, also known as baby teeth, is a natural and expected part of a child’s dental development. On average, children begin to lose their primary teeth between the ages of 6 and 7 years old, although this can vary. Girls may lose their baby teeth a bit earlier than boys. The process of losing baby teeth can continue until the age of 12 or 13, when all 20 primary teeth have been replaced by permanent teeth. It is important for parents to monitor their child’s dental development during this time and to ensure that they are practicing good oral hygiene habits to maintain the health of their new permanent teeth.
There are several factors that can affect the timing of tooth loss in children. Genetics play a significant role, as the age at which parents and siblings lost their teeth can be a good indicator of when a child will lose theirs. Nutrition and overall health also play a part, as children who consume a diet lacking in essential nutrients or have underlying health conditions may experience delayed tooth loss. Additionally, dental trauma or developmental abnormalities can also impact the timing of tooth loss. Overall, it’s important to understand that tooth loss is a natural process that varies from child to child and can be influenced by a variety of factors.
Monitoring tooth development is crucial to ensure that children’s teeth are developing correctly and that any issues are identified early on. As children grow, their teeth go through various stages of development, and monitoring this process allows parents and dentists to identify any abnormalities or potential issues. Early detection and intervention can prevent more serious problems from developing in the future, such as malocclusion or tooth decay. Additionally, tracking tooth development can help parents understand when their child is ready to start brushing and flossing independently and when they can expect their child to start losing baby teeth. Overall, being proactive in monitoring tooth development is essential for promoting good oral health and preventing future dental problems.
What to Expect During the ToothLosing Process

The tooth-losing process is a natural and gradual phenomenon that occurs in every child’s growth and development. Typically, children start losing their baby teeth around the age of six, and it continues until they reach their early teenage years. The process happens as the adult teeth start pushing the baby teeth, which then loosen and eventually fall out. It is a vital part of tooth development and a sign that adult teeth are ready to emerge. During the tooth-losing process, children may experience various symptoms such as pain, sensitivity, and discomfort. These symptoms are typical and may cause mild discomfort for a few days. Parents can help alleviate the pain by offering their child soft foods, such as yogurt and soup, and encouraging them to drink plenty of water. It is also essential to remind children to brush their teeth twice daily, floss, and rinse their mouth with saltwater to help prevent infection or other dental problems. Overall, parents should encourage their child to be patient and gentle with their teeth as they go through this natural process.
Loose primary teeth are a natural part of the tooth development process in children. As children grow, their primary teeth will start to become loose and wobbly, signaling that they are ready to fall out and make way for permanent teeth. Signs of loose primary teeth include a noticeable shift in the tooth’s position, increased spacing between teeth, and discomfort or pain when chewing or biting. Parents may also notice their child’s gums becoming swollen or red around the affected tooth. If a child’s primary teeth are not loose by the age of 6 or 7, it may be a sign of delayed tooth development and should be evaluated by a dentist.
Tooth loss can be a painful and uncomfortable process, but there are several ways to ease the discomfort. One of the most effective ways is to use over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Applying a cold compress to the affected area can also help to reduce swelling and numb the pain. Eating soft foods and avoiding hard or crunchy foods can also help to alleviate discomfort. Additionally, maintaining good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly can help to prevent infection and speed up the healing process. Finally, if the pain is severe or persists for more than a few days, it is important to consult with a dentist to ensure proper treatment and care.
Proper care for emerging permanent teeth is crucial in maintaining a healthy and beautiful smile. As these teeth start to erupt, it is important to brush them twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove any food particles that may be trapped between the teeth. Additionally, limiting sugary snacks and drinks can prevent tooth decay and cavities. Parents can also take their children to the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings to ensure that any potential issues are caught early and treated promptly. By taking these preventive measures, children can enjoy a lifetime of healthy teeth and gums.
Maintaining Good Oral Health

Maintaining good oral health is crucial for overall well-being. It is important to brush and floss regularly to prevent cavities and gum disease. Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste helps to remove plaque, which is a sticky film of bacteria that can cause tooth decay. Flossing daily helps to remove food particles and plaque from between teeth and under the gum line. In addition to brushing and flossing, it is important to visit the dentist regularly for cleanings and checkups. The dentist can detect any potential problems early and recommend appropriate treatment. In addition to regular brushing and flossing, there are other ways to maintain good oral health. Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar and high in calcium and vitamin D can help to strengthen teeth and bones. Drinking plenty of water also helps to rinse away food particles and bacteria. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also help to protect oral health. By taking care of your teeth and gums, you can enjoy a healthy smile for years to come.
Regular dental checkups are crucial for maintaining good oral health. These visits allow dentists to identify and treat any potential issues before they become more serious problems. During a checkup, a dentist will examine the teeth and gums, looking for signs of decay, gum disease, or other issues. They may also take x-rays to check for any problems below the surface. In addition to identifying and treating issues, regular dental checkups also allow for preventative measures, such as cleanings and fluoride treatments, which can help keep teeth healthy and strong. By prioritizing regular dental checkups, individuals can ensure that their teeth and gums stay healthy and strong, helping to prevent issues and maintain overall oral health.
Maintaining proper oral hygiene is essential for the health and strength of teeth. Brushing twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using a mouthwash can help prevent tooth decay and gum disease. A balanced diet that includes calcium-rich foods, such as milk and cheese, can also help in keeping teeth strong. Limiting sugary and acidic foods and drinks can also help prevent erosion of the enamel. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings can help detect any issues early on and prevent further damage. Additionally, wearing a mouthguard during sports or other physical activities can protect teeth from injury. By following these tips, one can maintain healthy and strong teeth throughout their lifetime.
Nutrition plays a vital role in the development and maintenance of teeth. The minerals and vitamins we obtain from our diet are necessary for the formation of strong and healthy teeth. Calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D are particularly important for the growth and mineralization of teeth. They help to strengthen the tooth enamel and make it more resistant to decay. A diet that is high in sugar and processed foods, on the other hand, can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease. It’s essential to maintain a healthy and balanced diet to support the growth and maintenance of healthy teeth. Additionally, regular dental checkups and proper oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing, are crucial for maintaining good oral health.
Understanding tooth development and the process of losing primary teeth is crucial for parents and caregivers. As children grow, their teeth change, and parents must be aware of the different stages of tooth development to provide appropriate care. The primary teeth play a vital role in the development of speech, jawbone, and permanent teeth. The process of losing primary teeth can be a stressful time for both parents and children, but knowing what to expect can alleviate anxiety. It’s essential to encourage good oral hygiene habits from an early age to ensure healthy teeth and gums throughout life. By understanding tooth development, parents can help their children maintain healthy teeth and gums and prevent dental problems.
Maintaining good oral hygiene and monitoring tooth development are crucial for ensuring that children have healthy teeth and gums throughout their lives. It is important for parents to be aware of the stages of tooth development in their children, as this will help them identify any potential problems early on. By teaching children good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing and flossing regularly, parents can help prevent cavities and other oral health issues. Regular dental checkups are also important, as dentists can identify any problems and provide treatment if necessary. With proper care and attention, children can enjoy healthy teeth and gums well into adulthood.
Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding tooth development is crucial for parents to ensure their child’s dental health. The process of losing baby teeth and the emergence of permanent teeth is a natural and exciting milestone for children. It typically begins between the ages of 5 to 7 years old and lasts until they are around 12 to 13 years old. However, it’s important to note that every child is unique, and the timeline can vary. Parents should keep an eye on their child’s dental health and make sure they are taking proper care of their teeth as they transition from baby teeth to permanent teeth. By doing so, they can ensure their child’s dental health for years to come.