Table of Contents
Parents weren’t good parents if they would not wish all the best to their children. Small children often cry to get attention, which immediately forces the parents (especially those young and inexperienced) to search for the causes of crying and ways to quickly calm the child. In order to calm the child, parents resort to various “means and methods” of which breastfeeding or putting pacifier or bottle of milk into baby’s mouth often proved to be the most effective. In those moments (especially at night), parents generally do not think about the possible adverse effects that may be hazardous to dental health of their children. In fact, breastfeeding and consumption of food and/or liquids that contain sugar, including milk or formula, may have permanent consequences on primary teeth, causing specific form of caries that in the academic literature are described as – bottle caries, infant caries, circular cavity, early childhood dental caries, baby bottle tooth decay, rampant caries etc.
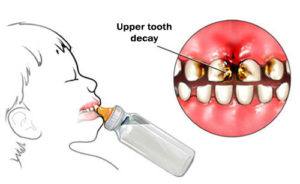
What is the baby bottle caries?
 Bottle caries is an infectious bacterial disease which is perhaps the simplest defined as tooth decay that occurs in the first three years of a child’s life. Most often these bacteria that cause infant caries are transmitted from mother or other family members to a small child. With a healthy diet, adequate rhythm of feeding and proper oral hygiene in the child of that age, the development of this disease usually can be successfully avoided. If the bottle caries is not noticed early enough, this form of caries can leave lasting effects that will be visible only in milk teeth, but may also affect the permanent dentition. In addition, damaged and non-functional milk teeth can have a detrimental effect on the physical and mental development of the child. Because of its bad look the child may feel inferior in comparison with its peers. In addition, these teeth disable normal digestion because the food can not be properly fragmented and chewed in the mouth. Often, due to lack of crown of front upper teeth, child’s speech becomes slurred.
Bottle caries is an infectious bacterial disease which is perhaps the simplest defined as tooth decay that occurs in the first three years of a child’s life. Most often these bacteria that cause infant caries are transmitted from mother or other family members to a small child. With a healthy diet, adequate rhythm of feeding and proper oral hygiene in the child of that age, the development of this disease usually can be successfully avoided. If the bottle caries is not noticed early enough, this form of caries can leave lasting effects that will be visible only in milk teeth, but may also affect the permanent dentition. In addition, damaged and non-functional milk teeth can have a detrimental effect on the physical and mental development of the child. Because of its bad look the child may feel inferior in comparison with its peers. In addition, these teeth disable normal digestion because the food can not be properly fragmented and chewed in the mouth. Often, due to lack of crown of front upper teeth, child’s speech becomes slurred.
For small babies check out our best baby teether review.
- I Got My 1st Tooth with Cute Tooth Baby Baby T-Shirt. Celebrate your 1st tooth in style.
- Printed in the USA
- 100% combed ringspun cotton
- Topstitched rib crewneck
- Double-needle stitched sleeves and bottom hem
- I Got My 1st Tooth with Cute Tooth Baby Baby Bib. Celebrate your 1st tooth in style.
- Our bibs are combed ring-spun cotton. Reinforced with a hook and loop closure. Created with only the finest and softest of materials that allow the little one to stay clean and comfortable.
- Printed with the best direct to garment printing technology using only ECO-FRIENDLY ink, creating a safe and comfortable bib.
- Our bibs are heat cured so the bibs are able to be washed countless of times and not show any fading, cracking, or loss of color.
- Inktastic, is a family owned business who prints all products in the USA with pride and integrity ensuring the best customer experience from start to finish.
- 25-piece dentist play set with realistic pretend play dental care essentials to give cleanings, treat cavities, and fit retainers and braces on an over-sized set of pretend teeth
- Includes set of pretend teeth, dry-erase marker, examination tools, toothbrush, toothpaste tube, dental rinse bottle and cup, 2 gauze pads, 3 tooth polish cups, top and bottom retainers and braces, mask, reusable ID tag on a lanyard, double-sided reusable activity card
- Use dry-erase marker to mark “decay” then clean with vibrating tool with interchangeable polishing and drill heads or toothbrush; back 4 teeth wiggle and lift to practice pretend extractions
- A fun and engaging way to teach good dental health practices, and to ease kids’ fears or feelings of stress associated with a visit to the dentist
- Makes a great gift for preschoolers, ages 3 to 6, for hands-on, screen-free play
How is baby bottle decay developed?
 In order to develop baby bottle decay, several preconditions must be met:
In order to develop baby bottle decay, several preconditions must be met:
1) there must be a tooth (host) present in the mouth on which caries may develop;
2) there must be bacteria in the mouth whose actions destroy tooth;
3) there must be a substrate (food for bacteria) – sugar (from milk, formula, food or sweet beverages);
4) enough time must pass to develop caries under the action of bacteria.
If only one of these preconditions is not fulfilled, decay will not develop.
 The first teeth in the mouth of a child usually occur after six months of age, and before the second year of life all primary teeth emerge. The oral cavity of a child initially does not contain the bacterium Streptococcus mutans, which is considered most responsible for early childhood tooth decay. It is believed that infection with this bacteria most commonly occurs because of close contact with saliva from family members (mother, father, brothers, sisters) which already contains Streptococcus mutans. Given that mother is most often in closest contact with the child in early childhood, she is most likely the main source of infection. Numerous research has shown that children whose mothers have a high level of this bacteria in the saliva, also have a high level of the same bacteria, unlike children whose mothers have low levels of bacteria. The higher the level of bacteria in the saliva, the greater the likelihood of caries. Since minimum amount of
The first teeth in the mouth of a child usually occur after six months of age, and before the second year of life all primary teeth emerge. The oral cavity of a child initially does not contain the bacterium Streptococcus mutans, which is considered most responsible for early childhood tooth decay. It is believed that infection with this bacteria most commonly occurs because of close contact with saliva from family members (mother, father, brothers, sisters) which already contains Streptococcus mutans. Given that mother is most often in closest contact with the child in early childhood, she is most likely the main source of infection. Numerous research has shown that children whose mothers have a high level of this bacteria in the saliva, also have a high level of the same bacteria, unlike children whose mothers have low levels of bacteria. The higher the level of bacteria in the saliva, the greater the likelihood of caries. Since minimum amount of 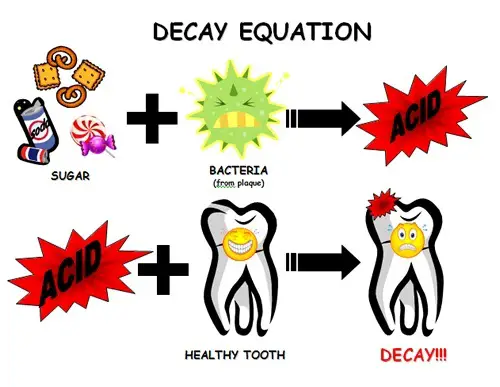 bacteria is required for the occurrence of caries, in practice this means that if a mother, father, brothers or sisters have carious teeth (and thus have a high level of Streptococcus mutans in saliva), a child will probably develop some form of tooth decay quite early. The substrate needed to feed the bacteria is all those remains of food and sugary liquids that stick to the teeth and remain in the oral cavity. Bacteria’s “favorite”, and therefore the most dangerous food are: candies, sweetened juices, milk/formula and refined carbohydrates, because they stick easily to the surface of teeth and long linger in child’s mouth, using as a food source for bacteria. In order to develop caries, it is necessary that the bacteria specified amount of time consume food remains on the surface of teeth. The released acids slowly begin to erode (demineralise) enamel surface of the tooth causing the first barely noticeable color change, which over time becomes more pronounced. At some point, after the color was changed, the first hole (the real caries lesion) appears.
bacteria is required for the occurrence of caries, in practice this means that if a mother, father, brothers or sisters have carious teeth (and thus have a high level of Streptococcus mutans in saliva), a child will probably develop some form of tooth decay quite early. The substrate needed to feed the bacteria is all those remains of food and sugary liquids that stick to the teeth and remain in the oral cavity. Bacteria’s “favorite”, and therefore the most dangerous food are: candies, sweetened juices, milk/formula and refined carbohydrates, because they stick easily to the surface of teeth and long linger in child’s mouth, using as a food source for bacteria. In order to develop caries, it is necessary that the bacteria specified amount of time consume food remains on the surface of teeth. The released acids slowly begin to erode (demineralise) enamel surface of the tooth causing the first barely noticeable color change, which over time becomes more pronounced. At some point, after the color was changed, the first hole (the real caries lesion) appears.
 General reasons and principles of caries development also apply with bottle caries. The occurrence of early childhood caries is accelerated due to prolonged contact of child’s teeth with milk during breastfeeding and/or feeding the child with formula or other sweetened beverages (sugar water, sweetened tea, juice etc.) before or during the night. Additionally, some mothers allow breastfeeding to continue for several hours, and often both the mother and the baby fall asleep while the child is still on the breast. That’s not good because the lactose, which was found in mother’s and cow’s milk, and sugars from sweetened liquids remain on the teeth surface for a long time causing cavities. In addition, during sleep the child has reduced secretion of saliva and a lower pH (acidic) in the oral cavity, which further helps the development of caries. Also, a detrimental effect on teeth has a habit of some parents to soothe a child by giving him a pacifier that has previously been dipped in honey or wallowed into sugar.
General reasons and principles of caries development also apply with bottle caries. The occurrence of early childhood caries is accelerated due to prolonged contact of child’s teeth with milk during breastfeeding and/or feeding the child with formula or other sweetened beverages (sugar water, sweetened tea, juice etc.) before or during the night. Additionally, some mothers allow breastfeeding to continue for several hours, and often both the mother and the baby fall asleep while the child is still on the breast. That’s not good because the lactose, which was found in mother’s and cow’s milk, and sugars from sweetened liquids remain on the teeth surface for a long time causing cavities. In addition, during sleep the child has reduced secretion of saliva and a lower pH (acidic) in the oral cavity, which further helps the development of caries. Also, a detrimental effect on teeth has a habit of some parents to soothe a child by giving him a pacifier that has previously been dipped in honey or wallowed into sugar.
 How to identify bottle caries?
How to identify bottle caries?
Although cavities normally do not occur so often on these teeth, bottle caries primarily affects upper front teeth and primarily their labial (outer), and then the palatal (inner) surface. The damages initially occur along the neck of the tooth, near the gum line, initially as a smaller demineralized areas off dimly white color, which quickly transform to real lesions and cover the entire tooth. When the entire tooth is covered with caries, it is the so-called circular bottle caries. The crown of the tooth that has been extensively affected by caries very quickly becomes completely destroyed, and the tooth root is often aligned with the level of the gums. The rest of the tooth has a tan color that stands out from the surrounding white milk teeth.
After the decay has destroyed the upper front four incisors, it can spread to the upper canines, and the biting surfaces of the upper molars. In contrast to the upper teeth, lower teeth are rarely affected by bottle caries, probably because they are closer to the tongue which, together with the saliva, mechanically removes dangerous food leftovers and sugary liquids from the teeth surface.
What are the consequences?
 Milk teeth are very important for normal growth and develop of the jaws, and the organism as a whole. They are used in the digestive process because they cut off and grind food. Insufficiently grained food can aggravate the digestive process in the lower digestive tract, and ultimately slow the overall growth of the child.
Milk teeth are very important for normal growth and develop of the jaws, and the organism as a whole. They are used in the digestive process because they cut off and grind food. Insufficiently grained food can aggravate the digestive process in the lower digestive tract, and ultimately slow the overall growth of the child.
Milk teeth have a phonetic role, because they are involved in the proper development of speech. The loss of the front teeth may disturb pronunciation of consonants “f”, “s”, “v” and “z” which leads to unclear and slurred speech of the child.
In advanced stage of bottle caries, shattered teeth become a potential source of various infections that may create numerous inconveniences such as pain, bleeding gums, bad breath and others, so going to the dentist can be extremely traumatic experience because of all the painful accompanying symptoms. It is often necessary to give antibiotics to the child. Also, primary (milk) teeth keep place for the proper display of the permanent successors. The premature loss of primary teeth can cause difficulties in eruption of permanent teeth, their abnormal position in the dental arch and compaction due to the inappropriate size of the jaw which becomes reduced for placement of permanent teeth.
 The longer the time between the loss of milk teeth and the usual time of their falling out, the degree of loss of space in the jaw will be greater. It is likely that a child who lost it’s baby teeth too early, in the future would have to carry some of orthodontic appliances for regulating the setting of permanent teeth in the dental arch. Loss of anterior primary teeth favors the development of bad habits such as tongue thrusting into the empty space. This can negatively affect the position of the newly spraught permanent incisors which become protruded by tongue that pushes them outside the dental arch.
The longer the time between the loss of milk teeth and the usual time of their falling out, the degree of loss of space in the jaw will be greater. It is likely that a child who lost it’s baby teeth too early, in the future would have to carry some of orthodontic appliances for regulating the setting of permanent teeth in the dental arch. Loss of anterior primary teeth favors the development of bad habits such as tongue thrusting into the empty space. This can negatively affect the position of the newly spraught permanent incisors which become protruded by tongue that pushes them outside the dental arch.
Primary teeth also have a psychological role in child development. If these teeth are extensively destroyed by decay, that often leaves a certain psychological effects on the child which, depending on the child’s character, can manifest either with withdrawal into hiimself or with increased activity of the child. Sometimes it happens that a child affected by bottle caries is jealous to his peers because of their healthy teeth, and ask parents to “buy” him new teeth. Parents should not allow that a child, because of his damaged teeth, feels neglected and less valuable. He should be comforted and consoled that, if properly and regularly brushes his teeth, new, bigger and more beautiful teeth will appear. Some of the best teeth brushing songs can help in that regard.
Due to the fact that in the modern society healthy and beautiful teeth are a symbol of youth, health, beauty and success, for most parents it is important that their children, from the earliest age of life, have beautiful teeth which can both be proud of. This perception of oral health, although very positive, also has a potentially negative side. In fact, in developed countries in North America and Europe, poor oral health in children (such as bottle caries, premature loss of teeth, acquired malocclusion, etc.) is considered a form of child abuse, which is called dental neglect. Negligence of child’s oral health can cause pain with lasting consequences, as with any other form of abuse. In reality this means that if the dentist notices that the child has poor oral health, he should notify the social service which would check whether the parents are able to care for their child. This is what all parents must pay attention to, because there is a large number of actions in which public encourages children to report any form of abuse.
 How to avoid bottle caries?
How to avoid bottle caries?
Although caries is the most common chronic disease in childhood, it can be completely prevented. To avoid baby bottle caries, the consumption of refined carbohydrates and the number of cariogenic bacteria in the oral cavity should be reduced with proper diet and regular oral hygiene. Additionally, it is good to apply fluorides because they increase tooth resistance to the action of acid generated by metabolism of bacteria. The dentist may smear the surface of the milk teeth with fluorides. It is also desirable that the child’s toothpaste contains fluorides or xylitol, and that parents control how much the toothpaste is placed on the toothbrush.
[thrive_text_block color=”purple” headline=””] In addition to these measures, there are several practical recommendations for avoiding baby bottle tooth decay:
- Avoid consumption of milk and sweet drinks at bedtime
- If the child falls asleep while breastfeeding, it should be separated from the breast and put to bed
- It is optimal to stop breastfeeding between 12 and 24 months of age, discontinuation of breastfeeding should be followed with drinking water and other beverages from a cup
- Do not give a bottle of any other beverage except water to the child and do not allow him to walk around with a bottle in his mouth; get him used to drink from a cup
- As soon as possible begin to decrease the share of liquid and increase the share of solid foods in the child’s daily diet (as recommended by some dentists as early as age of 6 months or when they get their first teeth)
- To reduce the number of cariogenic bacteria in the mouth, preferably even before the sprang of first tooth, once a day (at bedtime) child’s mouth should be mechanically cleaned of food debris with clean gauze or damp washcloth.
- Start brushing baby’s teeth on a daily basis when the first tooth appears to maintain oral hygiene and teeth, as long as the child is not able to so by himself.
- After the appearance of the first tooth, switch to lightly brushing the teeth and gums with a soft bristled toothbrush but with no toothpaste.
- Bring a child to the dentist no later than one year of age, because if there are defects in the teeth, they are not very advanced and can be easily repaired. [/thrive_text_block]
How to treat baby bottle tooth decay?
Early childhood dental caries is treated depending on the clinical picture at the time of the child’s dental visit. If the decay is discovered quite early, when there are only demineralized areas visible on the teeth in the form of white spots and lines, it is possible to recover teeth and to encourage their remineralization by the application of fluorides and changing child’s diet. In order for these procedures to be effective, it is necessary to visit the dentist to assess a child’s risk of developing caries and possibly recommend additional preventive and therapeutic measures. Special dental care is needed for children with autism.
 If the decay is so advanced that the teeth lesions are in the form of dark holes, the dentist will remove the softened and destroyed parts of the hard dental tissue to prevent its further progress. Depending on the size, the devastated areas of the teeth can be replaced with appropriate dental fillings. Although it is not usual practice, some dentists, especially in developed countries recommend making special crowns and covers for baby teeth.
If the decay is so advanced that the teeth lesions are in the form of dark holes, the dentist will remove the softened and destroyed parts of the hard dental tissue to prevent its further progress. Depending on the size, the devastated areas of the teeth can be replaced with appropriate dental fillings. Although it is not usual practice, some dentists, especially in developed countries recommend making special crowns and covers for baby teeth.
![]() If the tooth decay is affecting the pulp of the tooth, it is necessary to try to heal it in order to maintain the tooth in the jaw. However, if there are infections, abscesses or purulent fistula present, the tooth should be removed. It should be borne in mind that such conditions may leave a mark on the germ of permanent tooth which is close below, most often in the form of discoloration (changed color). In addition, because the milk teeth guard space for permanent teeth, their premature removal may lead to improper setup of permanent successors. Therefore, healthy baby teeth should be kept in the mouth until the eruption of permanent successors.
If the tooth decay is affecting the pulp of the tooth, it is necessary to try to heal it in order to maintain the tooth in the jaw. However, if there are infections, abscesses or purulent fistula present, the tooth should be removed. It should be borne in mind that such conditions may leave a mark on the germ of permanent tooth which is close below, most often in the form of discoloration (changed color). In addition, because the milk teeth guard space for permanent teeth, their premature removal may lead to improper setup of permanent successors. Therefore, healthy baby teeth should be kept in the mouth until the eruption of permanent successors.
Although the general practice dentist can provide dental care for a child, the removal of caries and dental treatment, especially in more complex cases such as when the child is less cooperative, is best to be left to the dentist specialist in pediatric dentistry who is specially trained and equipped to work with children. Although most procedures can be performed under the effect of local anesthesia, sometimes, especially with very small and/or uncooperative children, sedation or general anesthesia will be required.
It is desirable to bring the child to the dentist every 3 to 6 months in order to monitor the growth and development of the jaws. Specifically, if noticed that, due to the extracted deciduous teeth, disturbances in the normal development of the jaw are present, it is necessary to consult a dentist specialist in orthodontics in order to prevent the occurrence of major anomalies by usage of proper orthodontic appliances.
Conclusion
Bottle caries is a condition which emergence is entirely preventable, and that deprives both the child and parents of unpleasant emotional and health problems and potential financial costs in the future. The responsibility is on parents who need to be aware of the importance of oral health of their child. Along with daily oral hygiene care, parents should also provide the proper dental care by taking the child regularly to the dentist. Although even after bottle caries is cured the child can have normal permanent teeth, we should not forget that healthy and beautiful milk teeth precede healthy and beautiful permanent teeth.