When to Expect Your Puppy’s Retained Teeth to Fall Out: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcoming a new puppy into your home can be an exciting yet overwhelming experience. As a responsible pet owner, it is essential to be aware of your puppy’s dental health and understand when their baby teeth will fall out. Retained baby teeth can lead to numerous dental problems that may impact your furry friend’s overall well-being. Therefore, it is crucial to keep track of your puppy’s dental development and know when to expect their baby teeth to fall out. A puppy’s dental development is a gradual process that involves the eruption and shedding of baby teeth. Like humans, puppies are born without teeth, and their first set of baby teeth, also known as deciduous teeth, begin to emerge at around three to four weeks of age. These temporary teeth play a crucial role in your puppy’s early life, allowing them to explore and develop their jaw muscles. However, as your puppy grows, their baby teeth will eventually fall out, making way for their permanent teeth. Knowing when to expect your puppy’s retained teeth to fall out will help you ensure their dental health and provide them with the best possible care.
As a responsible pet owner, it’s crucial to know when your puppy’s teeth will fall out. Retained baby teeth can cause various dental issues and even lead to infections or gum diseases. It is also essential to monitor your puppy’s oral health as they grow up, and knowing when their baby teeth fall out can help you identify any potential problems early on. Moreover, if your puppy’s baby teeth do not fall out on their own, you might need to consult a veterinarian to have them removed. By keeping track of your puppy’s dental development, you can ensure that they have healthy teeth and gums throughout their lives.
The puppy teething process typically begins when a puppy is around three to four months old and can last up to eight months. During this time, puppies will experience discomfort and itching in their mouths as their baby teeth loosen and fall out, making way for their permanent teeth. As a result, puppies will often chew on objects to alleviate the discomfort, which can lead to destructive behavior if not managed properly. It is essential to provide your puppy with appropriate chew toys and to supervise their chewing behavior to prevent them from damaging furniture or other belongings. Additionally, it is crucial to maintain good oral hygiene during this process to prevent any potential dental issues. With patience and proper care, your puppy will emerge with a healthy and beautiful set of adult teeth.
Deciduous Teeth

Deciduous teeth, also known as milk teeth or baby teeth, are the first set of teeth that puppies develop. These teeth are usually fully developed by the time a puppy is 6 to 8 weeks old and start falling out between 12 to 16 weeks of age. The deciduous teeth consist of 28 teeth, including incisors, canines, and premolars. They play an important role in a puppy’s life as they help with eating, chewing, and teething. As the puppy grows, these teeth are replaced by permanent teeth that are stronger and more durable. It is important to keep an eye on your puppy’s deciduous teeth as they can cause problems if they don’t fall out on their own. Sometimes, the permanent teeth start growing before the deciduous teeth fall out, causing the puppy to have two sets of teeth in one place. This can lead to crowding and misalignment of teeth, which can cause dental problems in the future. If you notice that your puppy’s retained deciduous teeth are not falling out, it is important to consult a veterinarian who can help remove them to prevent any dental issues.
Deciduous teeth, also known as baby teeth or milk teeth, are the first set of teeth that puppies develop. These teeth are temporary and will eventually be replaced by their permanent teeth. Puppies typically have 28 deciduous teeth, which start to emerge at around 3-4 weeks of age and should all be present by 8 weeks of age. The purpose of these teeth is to help puppies chew their food and develop their jaw muscles. As puppies grow and their permanent teeth start to come in, the roots of their deciduous teeth will begin to dissolve, causing them to become loose and eventually fall out. This process typically starts around 12-16 weeks of age and should be complete by around 6 months of age. It’s important to monitor your puppy’s teeth during this time to ensure that their permanent teeth are coming in properly and that any retained baby teeth are addressed by a veterinarian.
Deciduous teeth, also known as baby or milk teeth, are the first set of teeth that puppies develop. These teeth are essential for chewing, biting, and playing. As puppies grow, their deciduous teeth will start to fall out to make way for their permanent teeth. Typically, this process begins around 12 weeks of age and can continue until the puppy is about six months old. The first teeth to fall out are the incisors, followed by the premolars and molars. It’s essential to keep an eye on your puppy’s teeth during this time as retained baby teeth can cause dental problems in the future. In case of any concerns or abnormality, it’s best to consult a veterinarian.
The process of deciduous teeth falling out in puppies may take anywhere from 3 to 8 months, depending on the breed and individual characteristics of the dog. The incisors are usually the first to fall out, followed by the canines and premolars. The molars are typically the last to go, and may not fall out until the puppy is around 6 to 8 months old. It’s important to note that retained deciduous teeth can cause problems such as gum irritation, tooth decay, and improper alignment of permanent teeth. Therefore, it’s crucial to monitor your puppy’s dental health and consult with a veterinarian if any issues arise.
Permanent Teeth
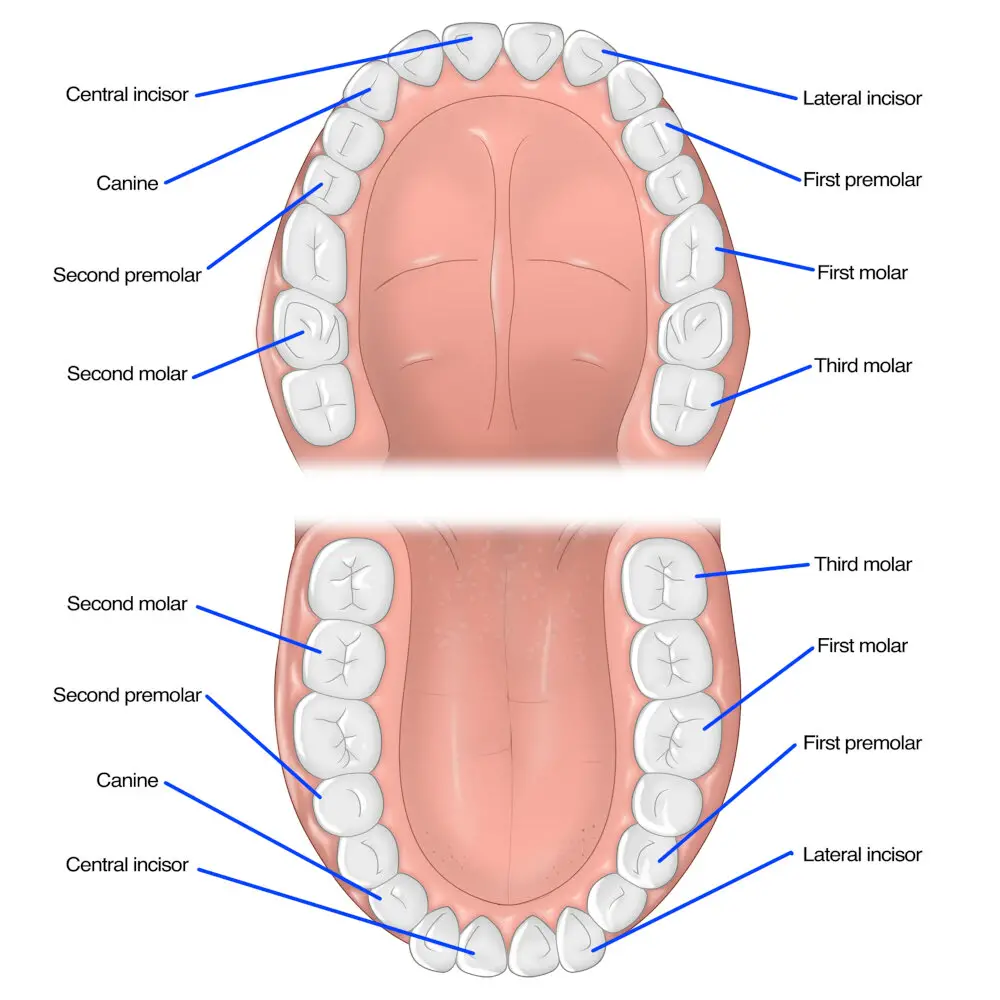
Permanent teeth refer to the set of teeth that replace the temporary milk teeth in humans and animals. These teeth are also known as adult teeth and are meant to last a lifetime. Unlike milk teeth, permanent teeth are larger, stronger, and more durable, allowing them to withstand the wear and tear of daily use. They are also designed to perform a variety of functions, such as biting, chewing, and grinding food, and are essential for maintaining good oral health. There are 32 permanent teeth in a typical adult human, including eight incisors, four canines, eight premolars, and twelve molars. The eruption of permanent teeth is a gradual process that begins around the age of six and continues until the late teenage years. During this time, the roots of the milk teeth are gradually absorbed, making room for the permanent teeth to emerge. The first permanent teeth to emerge are usually the molars, which appear behind the last milk teeth. Over the next few years, the remaining teeth gradually emerge, and by the age of 18, most people have a full set of permanent teeth. However, in some cases, the eruption of permanent teeth may be delayed or interrupted, leading to a variety of dental problems. Therefore, it is important to monitor the development of permanent teeth and seek professional dental care if any issues arise.
Permanent teeth are the set of teeth that replace the primary or baby teeth. They are the final set of teeth that a person will have for the rest of their life, and they usually begin to emerge during adolescence. There are 32 permanent teeth, which include four wisdom teeth that may or may not develop. These teeth are larger and stronger than the primary teeth and have a more complex structure that allows them to chew and grind food effectively. The permanent teeth are also more resistant to decay and damage, but proper dental hygiene is still essential to maintain their health and longevity.
Permanent teeth are a crucial part of a puppy’s development, as they replace the baby teeth and are essential for proper chewing and digestion. These teeth typically begin to emerge when a puppy is around 4-6 months old, starting with the incisors and followed by the premolars and molars. The timing of permanent teeth eruption can vary depending on the breed, with smaller breeds typically having earlier eruption times than larger breeds. It’s important for pet owners to monitor their puppy’s dental health during this time, looking out for retained baby teeth or any signs of discomfort or pain. By staying on top of dental care, owners can ensure that their puppy’s permanent teeth come in healthily and properly aligned.
Like humans, dogs also have two sets of teeth, the baby teeth, and the permanent teeth. Puppies start developing their permanent teeth at around three months old, and the process usually takes about four months to complete. By the age of seven months, most dogs should have all of their permanent teeth fully grown in. However, this timeline can vary depending on the breed and individual dog. It’s essential to keep an eye on your puppy’s teeth development as retained baby teeth can cause dental problems, leading to infections and discomfort for your furry friend.
Warning Signs

As a pet owner, it is important to be aware of the warning signs that may indicate a problem with your puppy’s retained teeth. One of the most noticeable signs is bad breath, which can be a sign of infection or decay in the retained teeth. Other warning signs may include swollen or bleeding gums, difficulty eating or chewing, excessive drooling, or a change in your puppy’s behavior. If you notice any of these warning signs, it is important to seek veterinary care for your puppy as soon as possible. Ignoring warning signs of retained teeth in your puppy can lead to serious health complications down the road. In addition to causing discomfort and pain, retained teeth can lead to infections, abscesses, and tooth decay. In severe cases, untreated retained teeth can even lead to bone loss or damage to surrounding teeth. By being vigilant and seeking veterinary care at the first sign of trouble, you can help ensure a healthy and happy life for your furry friend.
As a pet owner, it’s essential to keep an eye on your puppy’s dental health. Although it’s normal for puppies to lose their baby teeth, sometimes they may retain their milk teeth, leading to dental issues. Some warning signs that your puppy’s teeth are not falling out on schedule include bad breath, inflamed or bleeding gums, difficulty eating or chewing, and misaligned or crowded teeth. Additionally, you may also notice your puppy chewing or scratching excessively, avoiding hard food or toys, or showing signs of pain or discomfort while eating. If you observe any of these signs, it’s crucial to consult a veterinarian to address the issue before it escalates and causes long-term dental problems.
When your puppy’s teeth don’t fall out on time, it can lead to several dental problems like overcrowding, misalignment, and even gum infections. Retained baby teeth can cause adult teeth to grow in wrong positions, leading to malocclusions that can result in difficulty chewing, biting, and even speaking. Additionally, retained teeth can create pockets in the gums where food can get trapped, leading to the buildup of bacteria and plaque, which can eventually cause gum disease. It’s crucial to keep an eye on your puppy’s teeth and to consult with a veterinarian if you notice any issues with your pup’s dental health. Early intervention can prevent further complications and ensure your pup has a healthy, happy smile for years to come.
It is important to consult with your veterinarian if you suspect that your puppy’s retained teeth are not falling out in a timely manner. Retained teeth can cause a variety of dental problems, such as overcrowding and misalignment, which can lead to more serious health issues. Your veterinarian can determine if your puppy’s retained teeth need to be extracted or if they will fall out naturally. Additionally, your veterinarian can provide advice on proper dental care for your puppy, including brushing and regular check-ups, to prevent future dental issues. It is always better to be proactive when it comes to your puppy’s dental health, and consulting with your veterinarian can help ensure that your puppy’s teeth stay healthy and strong.
How to Help Your Puppy through the Teething Process
The teething process can be a challenging time for both puppies and their owners. It’s essential to understand that teething is a natural process that all puppies go through, and there are things you can do to help your furry friend through this period. One of the best ways to help your puppy through the teething process is to provide them with plenty of chew toys. Puppies love to chew, and it helps to alleviate the pain and discomfort associated with teething. Make sure that the toys you provide are durable and safe for your pup to chew on. You don’t want them to swallow anything they shouldn’t or hurt themselves in the process. Another way to help your puppy through the teething process is to give them frozen treats. Frozen carrots or other vegetables can be a great option, as they are healthy and help to numb the gums. You can also freeze a damp washcloth and give it to your pup to chew on. The cold temperature can help to soothe their sore gums. Be sure to supervise your puppy when giving them frozen treats to ensure they don’t choke or have any adverse reactions. With a little patience and care, you can help your puppy through the teething process and ensure they grow up to be healthy, happy dogs.
During the teething process, puppies experience discomfort due to the eruption of their adult teeth. You can help your puppy through this process by providing them with appropriate chew toys, such as frozen carrots or KONG toys filled with peanut butter. These toys will not only alleviate their discomfort but also help to strengthen their jaw muscles. Additionally, you can provide your puppy with plenty of attention and affection to help them feel calm and reassured during this difficult time. It’s important to monitor your puppy’s chewing habits to ensure they are not damaging their teeth or ingesting harmful objects. By taking these steps, you can help your puppy through the teething process and ensure they have a healthy and happy transition to adult teeth.
It’s essential to provide your puppy with safe chew toys and treats to help them alleviate their teething discomfort and prevent destructive chewing behavior. Some great options for chew toys include KONGs, Nylabones, and rope toys. These toys are durable, safe, and can help clean your puppy’s teeth. When it comes to treats, it’s best to choose options that are specifically designed for puppies, like soft chews or small biscuits. Avoid giving your puppy human food or treats that are too hard, as they can break their teeth or cause digestive issues. Always supervise your puppy when they’re chewing to ensure their safety.
During the teething process, it’s important to avoid giving your puppy hard and crunchy treats, as they can damage their teeth and gums. It’s also important to avoid giving them old or stale treats, as they may be too hard for their teeth to handle. Additionally, you should avoid playing rough with your puppy, as this can cause them to accidentally bite down too hard on their own teeth, leading to damage or injury. Finally, avoid giving your puppy toys that are too hard or abrasive, as they can cause damage to their teeth or gums. By being mindful of these potential hazards, you can help ensure that your puppy’s teething process is as comfortable and safe as possible.
In summary, understanding the timeline for your puppy’s retained teeth to fall out is crucial for their oral health. Puppies typically begin losing their baby teeth at around 3-4 months old, and the process is usually complete by 6-8 months old. However, there are cases where retained baby teeth can cause problems such as overcrowding, misalignment, and gum disease. Therefore, it’s essential to monitor your pup’s teeth and seek veterinary care if necessary. Additionally, providing your puppy with appropriate chew toys and a healthy diet can aid in the natural process of teeth shedding. Remember, maintaining your puppy’s oral health is an investment in their overall well-being.
Monitoring your puppy’s teeth is crucial to their overall health and well-being. Just like humans, dogs can suffer from dental issues such as gum disease, tooth decay, and even tooth loss. By regularly checking your puppy’s teeth, you can catch any potential problems early on and prevent them from progressing into more serious issues. It’s also important to establish a dental care routine early on in your puppy’s life, including regular brushing and dental cleanings. By taking care of your puppy’s teeth, you can ensure that they stay happy, healthy, and pain-free throughout their life.
Caring for your puppy’s teeth is crucial to their overall health and well-being. After their retained teeth have fallen out, it’s important to continue a regular dental hygiene routine to maintain healthy teeth and gums. This includes brushing their teeth regularly with a dog-specific toothpaste, providing them with dental chews and toys to help remove plaque and tartar buildup, and scheduling regular dental checkups with your veterinarian. Additionally, feeding your puppy a healthy and balanced diet can also contribute to their dental health. By taking these proactive steps, you can help ensure that your puppy maintains healthy teeth and gums for years to come.
Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding when to expect your puppy’s retained teeth to fall out is crucial for their dental health and overall well-being. As a responsible pet owner, it is essential to keep a close eye on your puppy’s teeth and schedule regular visits with the veterinarian. By following the comprehensive guide outlined in this article, you can ensure that your furry friend transitions smoothly from puppyhood to adulthood with a healthy set of teeth. Remember, prevention is key, and taking proactive steps towards your puppy’s dental health will not only keep their teeth strong but will also prevent future dental problems. So, keep the above tips in mind and give your puppy the best chance for a healthy and happy life.