Why 28 Teeth? Understanding the Science Behind Your Adult Dentition
Your adult dentition is an essential part of your overall health, and it’s important to understand why you have the 28 teeth that make up your smile. Our teeth are not only responsible for helping us bite and chew our food, but they also play a crucial role in our speech and facial appearance. However, have you ever wondered why we have precisely 28 teeth as adults? The science behind our adult dentition is quite fascinating and involves a complex interplay between genetics, evolution, and lifestyle factors. Our teeth are a product of millions of years of evolution and have adapted to meet the changing needs of our diets and lifestyles. Understanding the underlying science behind our teeth can help us appreciate their importance and take better care of them to maintain optimal oral health. In this article, we will explore the reasons behind why we have 28 teeth and delve deeper into the science of our adult dentition.
The Anatomy of Adult Teeth
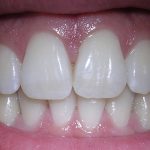
The adult dentition is composed of 28 teeth, with 14 in the upper jaw and 14 in the lower jaw. Each tooth has its own unique anatomy, with different structures and functions. The visible portion of the tooth, known as the crown, is covered by a hard, protective layer of enamel. Underneath the enamel is another hard tissue called dentin, which surrounds the soft, living tissue known as the pulp. The pulp contains nerves and blood vessels that provide the tooth with nutrients and sensation. The roots of the tooth extend into the jawbone and are anchored by periodontal ligaments that hold the tooth in place. Adult teeth are classified into four types: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. Incisors are located in the front of the mouth and have a sharp, flat edge for cutting food. Canines are the longest teeth and are designed for tearing and grasping food. Premolars have two cusps, or points, on their biting surface and are used for crushing and grinding food. Finally, molars are the largest teeth and have several cusps on their biting surface. They are responsible for grinding and pulverizing food before it is swallowed. Understanding the anatomy of adult teeth is important for maintaining good dental health and preventing tooth decay and gum disease.
Adult teeth, also known as permanent teeth, come in four different types: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. Incisors are the eight front teeth in the upper and lower jaw, and their primary function is to bite and cut food. Canines, also called cuspids, are the four pointed teeth located at the corners of the mouth, and they help tear tough foods like meat. Premolars, or bicuspids, are the teeth located between the canines and molars, and they are used for chewing and grinding food. Finally, molars are the largest teeth located at the back of the mouth, and their primary function is to crush and grind food into small pieces. Understanding the different types of adult teeth can help people take better care of their oral health and maintain a healthy, functional smile.
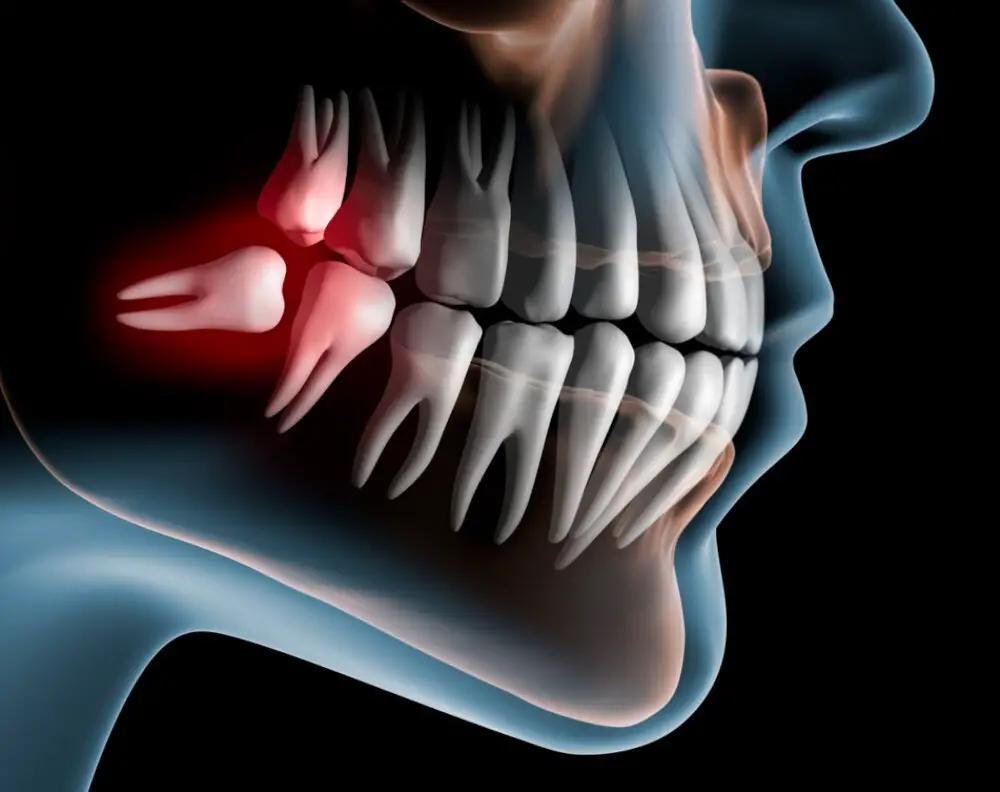
The human adult dentition consists of 28 teeth, each with a unique structure and function. Incisors are the front teeth used for biting and cutting food. Canines or cuspids are located next to the incisors and have pointed tips used for tearing and shredding food. Premolars or bicuspids are situated between the canines and molars and have two cusps for crushing and grinding food. Molars are the largest teeth located at the back of the mouth, used for crushing and grinding food. Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the final set of teeth to erupt, typically between ages 17 and 25, and are often removed due to lack of space or impaction. Each tooth is composed of different layers, including enamel, dentin, and pulp, and plays a vital role in the digestive process. Understanding the structure and function of each tooth is crucial for maintaining proper oral health and hygiene.
Adult teeth differ from baby teeth in various ways, including size, number, and composition. Adults typically have 28 teeth, while babies have 20. Adult teeth are also larger and stronger than baby teeth, and their roots are longer and more firmly anchored in the jawbone. In contrast, baby teeth have shorter roots and are designed to fall out eventually as the jaw grows and makes room for permanent teeth. Additionally, adult teeth are made up of enamel, dentin, and pulp, while baby teeth have thinner enamel and less dentin. This makes adult teeth more resistant to decay and damage, but also means that problems with adult teeth can be more serious and require more extensive treatment. Understanding the differences between baby and adult teeth can help you take better care of your dental health and appreciate the fascinating science behind your smile.
The Development of Adult Teeth

The development of adult teeth is a complex and fascinating process that begins long before the teeth actually emerge from the gums. It all starts in the womb, where the primary teeth begin to form around the sixth week of pregnancy. These teeth, also known as baby teeth or deciduous teeth, will eventually be replaced by the permanent teeth that we all have as adults. The process of tooth development continues throughout childhood and into adolescence, as the permanent teeth gradually take the place of the primary teeth. The development of adult teeth is a highly regulated process that involves the interaction of many different genes and signaling pathways. It is also influenced by a wide range of environmental factors, including nutrition, hormones, and stress. As the teeth develop, they go through a number of stages, from the initial formation of the tooth buds to the eruption of the teeth through the gums. Along the way, the teeth are shaped and reshaped by the forces of the tongue, lips, and cheeks, as well as by the actions of the muscles and bones in the jaw. Ultimately, the development of adult teeth is a testament to the incredible complexity and adaptability of the human body.
The process of tooth development begins in the embryonic stage, where cells in the dental lamina divide and form the primary teeth buds. These buds then develop into the deciduous teeth, which erupt around six months to two years of age. As the child grows, the permanent teeth buds form behind the primary teeth, and eventually, the primary teeth are shed and replaced by the permanent teeth. The permanent teeth continue to develop throughout childhood and adolescence, with the last teeth, the third molars or wisdom teeth, typically erupting between the ages of 17 and 25. The stages of tooth development are a complex and fascinating process that involves numerous genetic and environmental factors.
Tooth development is a complex process that can be influenced by various factors. Genetics plays a significant role in determining the size, shape, and number of teeth that an individual will have. Nutritional deficiencies, such as a lack of calcium or vitamin D, can also hinder proper tooth development. Environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins or radiation, can lead to abnormalities in tooth formation. Additionally, certain medications and medical conditions can affect tooth development, including conditions that affect the endocrine system or damage the tooth buds during prenatal development. It is important to maintain good oral health and seek professional dental care to ensure proper tooth development and prevent dental issues.
The development of teeth is a complex process that is regulated by various genetic and environmental factors. Genetics plays a crucial role in determining the size, shape, and number of teeth in an individual. The genes responsible for tooth development are expressed during embryonic development, and any alterations or mutations in these genes can lead to abnormalities in tooth formation. For example, mutations in the MSX1 and PAX9 genes have been linked to hypodontia, a condition where an individual develops fewer teeth than normal. Further research on the genetic basis of tooth development is necessary to understand the underlying mechanisms and potential treatments for dental abnormalities.
The Importance of Adult Teeth
Adult teeth are a crucial part of the human body that serve several essential functions. As the name suggests, adult teeth are permanent teeth that replace the baby teeth that fall out during childhood. These teeth are designed to last a lifetime and perform several critical roles that help maintain overall health. Adult teeth are responsible for chewing, biting, and breaking down food, which is an essential step in the digestive process. They also help maintain the structure of the jaw and facial bones, which can impact overall appearance and confidence. In addition, adult teeth contribute to speech development and play a role in maintaining oral health by keeping the gums and surrounding tissues healthy. Furthermore, adult teeth are essential for maintaining overall health and wellbeing. Poor dental health has been linked to several health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. Maintaining healthy adult teeth is critical to reducing the risk of these health conditions and ensuring overall health and wellbeing. Regular dental checkups and cleanings are essential to maintaining healthy adult teeth, as they can help detect and prevent dental issues before they become more serious. Overall, adult teeth are a critical part of the human body that plays a crucial role in maintaining both oral and overall health.
Adult teeth play a vital role in the process of chewing and digestion. The incisors, canines, and premolars work together to break down food into smaller pieces, while the molars crush and grind the food into a soft pulp. This pulp is then mixed with enzymes and saliva which begins the process of digestion in the mouth. The tongue then pushes the food towards the back of the mouth where it is swallowed and travels down the esophagus to the stomach. Without the proper alignment and function of our adult teeth, the process of chewing and digestion can be disrupted, leading to digestive problems and malnutrition. Therefore, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene and address any dental issues promptly to ensure proper function of our adult dentition.
Missing or damaged adult teeth can have a significant impact on a person’s life. From a functional standpoint, missing teeth can make it difficult to eat certain foods and can cause speech difficulties. In addition, missing or damaged teeth can impact a person’s self-esteem and self-confidence. The appearance of a person’s smile can be affected, and they may feel embarrassed or self-conscious about their teeth. Furthermore, missing teeth can lead to bone loss in the jaw, which can cause the surrounding teeth to shift and lead to further dental problems. It is important for individuals to take care of their teeth and seek dental treatment if they experience any issues with their adult dentition.
Maintaining good oral health is not only essential for a bright smile and fresh breath, but it also has a significant impact on overall health. Poor oral hygiene can lead to a range of health problems, such as gum disease, tooth decay, and oral cancer, which can affect the entire body. Research has shown that oral health is linked to cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory infections, and even dementia. The mouth is the gateway to the body, and harmful bacteria that enter the bloodstream from the mouth can cause inflammation and increase the risk of developing chronic diseases. Therefore, taking care of your teeth and gums through regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups is crucial for maintaining good overall health and well-being.
Maintaining Healthy Adult Teeth
Maintaining healthy adult teeth is crucial for overall health and well-being. A healthy mouth and teeth can prevent various diseases and infections, boost confidence, and allow for proper chewing and digestion. The first step in maintaining healthy teeth is to practice good oral hygiene. Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing regularly, and using mouthwash can help remove plaque and bacteria that can cause tooth decay and gum disease. It is also important to maintain a healthy diet, avoiding sugary and acidic foods and drinks that can erode tooth enamel. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are also essential for maintaining healthy teeth. A dentist can detect and treat any dental issues early on, such as cavities or gum disease, before they become more serious and require more extensive treatment. Additionally, practicing good oral hygiene and visiting the dentist regularly can help prevent bad breath, tooth loss, and other dental problems. By taking care of your teeth and gums, you can enjoy a healthy, beautiful smile for years to come.
Good oral hygiene is crucial to maintaining overall health and preventing dental problems. The mouth is a gateway to the rest of the body, and poor oral hygiene can lead to a range of health issues, including gum disease, tooth decay, and even heart disease. By brushing and flossing regularly, as well as visiting the dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings, individuals can ensure their teeth and gums stay healthy. Additionally, a healthy mouth can make a significant difference in one’s confidence and self-esteem, as a bright, white smile can improve one’s appearance and overall quality of life. In short, good oral hygiene is an essential part of maintaining overall health and well-being.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial to keeping your adult teeth healthy. Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily can help prevent tooth decay and gum disease. It’s also important to limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks, as they can erode tooth enamel. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings every six months can detect any potential issues early on and prevent them from becoming more serious. Additionally, wearing a mouthguard while playing sports can protect your teeth from injury. By following these tips, you can ensure that your adult teeth stay healthy and strong for years to come.
Regular dental checkups play a crucial role in maintaining good oral health. These routine visits allow dentists to identify and treat any dental issues before they become more serious or painful. During a dental checkup, dentists can conduct a thorough examination of the teeth, gums, and mouth, looking for signs of cavities, gum disease, and even oral cancer. In addition, regular cleanings can help remove plaque and tartar buildup that can lead to tooth decay and gum disease. Overall, investing in regular dental checkups can help prevent more serious dental issues down the road and keep your smile healthy and bright.
In the article \Why 28 Teeth: Understanding the Science Behind Your Adult Dentition,\ the author explains the importance and function of our adult teeth. It is revealed that the number of teeth in adults is 28, which includes four types of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. The incisors are used for biting and cutting food, while the canines are for tearing and gripping. The premolars and molars are for grinding and crushing food. The article also discusses the anatomy of the teeth, including the enamel, dentin, and pulp, and how they work together to protect and nourish our teeth. The importance of regular dental care is emphasized, as well as the role of genetics in determining the size and shape of our teeth. Overall, the article provides a comprehensive understanding of the science behind our adult dentition and the vital role our teeth play in our overall health and well-being.
Taking care of your adult teeth is crucial for maintaining good oral health and overall well-being. Adult teeth are permanent and must last a lifetime, unlike primary teeth that fall out and are replaced. They play a vital role in biting, chewing, and speaking, as well as contributing to the shape of your face. Neglecting to care for your adult teeth can lead to a wide range of dental problems, including cavities, gum disease, and tooth loss. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups can help prevent these issues and ensure the longevity of your adult teeth. In addition, good oral hygiene has been linked to better overall health, with studies suggesting a connection between oral health and conditions such as heart disease and diabetes. Therefore, taking care of your adult teeth is not only important for your dental health but also for your overall health and well-being.
In conclusion, understanding the science behind your adult dentition and the function of your 28 teeth is crucial for maintaining good oral health. Your teeth play a vital role in chewing, speaking, and even affecting your overall appearance. Therefore, it is essential to adopt healthy oral hygiene habits, such as regular brushing and flossing, along with a balanced diet, to keep your teeth and gums healthy. It is also essential to visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings to prevent any potential dental issues. By taking care of your teeth, you can ensure a healthy and beautiful smile for years to come.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the number of teeth in a human adult’s dentition has evolved over time as a result of various factors such as diet, genetics, and natural selection. The 28 teeth in an adult dentition provide a balance between optimal chewing efficiency and the space required for the growth and positioning of these teeth. Each tooth plays a crucial role in the digestive process, and the loss of even a single tooth can have detrimental effects on overall health. Understanding the science behind our adult dentition reinforces the importance of proper dental hygiene, regular checkups, and prompt treatment of any dental issues to maintain optimal oral health and overall well-being.